Saturday, 29 November 2014
WIS Ecosystem Observation
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1SwBCLeStwTL4mcTHbtiXFbto5AcnuqCjmwphWheX-Qg/edit
Wednesday, 26 November 2014
Water Pollution
"Pollution" means hazardous wastes and other pollutants. Including sludge or residue from it that was dumped from the pollution source. Or existing in the natural environment. Which caused a negative impact on the environment and harm the health of the people. Including radiation, heat, sound, light, vibration, odor that has occurred or is released from the pollution source.
"Pollution" means the environmental conditions change or contaminated by pollution. This makes the quality of environmental degraded, such as water pollution, air pollution. And soil pollution
"Waste" means waste that is in a state of flux. Including mixed pollutant Or contamination is
the liquid
Types of water pollution
1. Nutrients Pollution
Some wastewater, fertilizers and sewage contain high levels of nutrients. If they end up in water bodies, they encourage algae and weed growth in the water. This will make the water undrinkable, and even clog filters. Too much algae will also use up all the oxygen in the water, and other water organisms in the water will die out of oxygen starvation.
2. Surface water pollution
Surface water includes natural water found on the earth's surface, like rivers, lakes, lagoons and oceans. Hazardous substances coming into contact with this surface water, dissolving or mixing physically with the water can be called surface water pollution.
3. Oxygen Depleting
Water bodies have micro-organisms. These include aerobic and anaerobic organisms. When to much biodegradable matter (things that easily decay) end up in water, it encourages more microorganism growth, and they use up more oxygen in the water. If oxygen is depleted, aerobic organisms die, and anaerobic organism grow more to produce harmful toxins such as ammonia and sulfides.
4. Ground water pollution
When humans apply pesticides and chemicals to soils, they are washed deep into the ground by rain water. This gets to underground water, causing pollution underground.
5. Microbiological
In many communities in the world, people drink untreated water (straight from a river or stream). Sometimes there is natural pollution caused by micro-organisms like viruses, bacteria and protozoa. This natural pollution can cause fishes and other water life to die. They can also cause serious illness to humans who drink from such waters.
6. Suspended Matter
Some pollutants (substances, particles and chemicals) do not easily dissolve in water. This kind of material is called particulate matter. Some suspended pollutants later settle under the water body. This can harm and even kill aquatic life that live at the floor of water bodies.
7. Chemical Water Pollution
Many industries and farmers work with chemicals that end up in water. This is common with Point-source Pollution. These include chemicals that are used to control weeds, insects and pests. Metals and solvents from industries can pollute water bodies. These are poisonous to many forms of aquatic life and may slow their development, make them infertile and kill them.
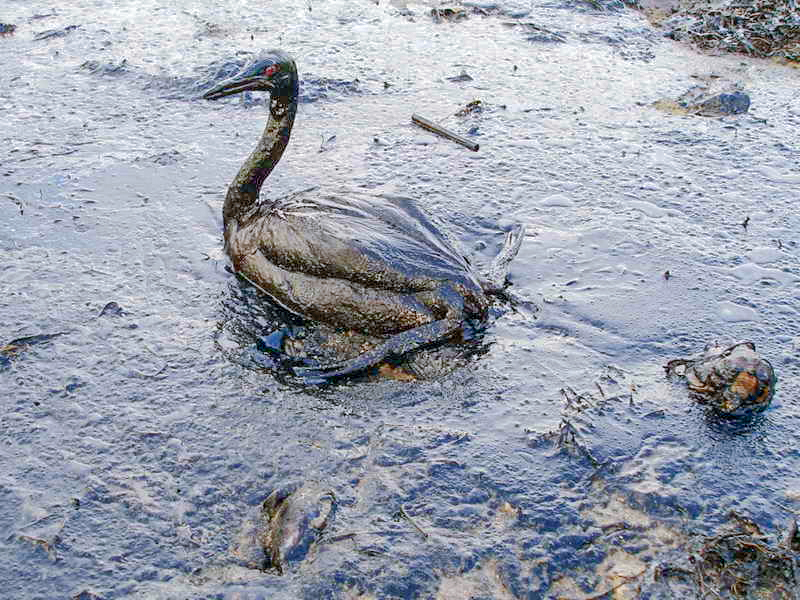
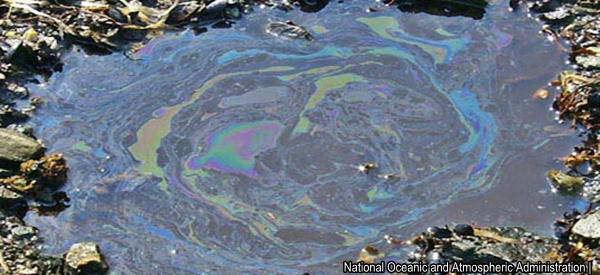
8. Oil Spillage
Oil spills usually have only a localized effect on wildlife but can spread for miles. The oil can cause the death to many fish and get stuck to the feathers of seabirds causing them to lose their ability to fly.
Water Pollution
The Ciliwung River is 119km long and passes through the Bogor Province, Depok District and the city of Jakarta in Indonesia. It is renowned for being one of the most heavily polluted rivers in the world. Many Indonesian citizens are forced to live by the river because it is all they can afford. Of the ten million people in Jakarta, half live on less than US$2 per day, and a large percentage of those people live along the Ciliwung. People that live along the Ciliwung use it for everything from washing themselves to cleaning clothes and dishes, to swimming. Contamination from human waste is the biggest cause of pollution in the Ciliwung. There is no organised rubbish collection for this area, so waste ends up in the river. Because they cannot afford clean drinking water, many of the residents are forced to boil and drink the water from the river, causing a raft of health problems. In 2009, a group of residents from Bogor with growing concerns about the river formed the Community Care for Ciliwung group ('Komunitas Peduli Ciliwung, or KPC). The group focuses its acitivities on picking up trash from the river every Saturday morning, and also facillitates other community activities such as tree planting days
"Pollution" means the environmental conditions change or contaminated by pollution. This makes the quality of environmental degraded, such as water pollution, air pollution. And soil pollution
"Waste" means waste that is in a state of flux. Including mixed pollutant Or contamination is
the liquid
Types of water pollution
1. Nutrients Pollution
Some wastewater, fertilizers and sewage contain high levels of nutrients. If they end up in water bodies, they encourage algae and weed growth in the water. This will make the water undrinkable, and even clog filters. Too much algae will also use up all the oxygen in the water, and other water organisms in the water will die out of oxygen starvation.
2. Surface water pollution
Surface water includes natural water found on the earth's surface, like rivers, lakes, lagoons and oceans. Hazardous substances coming into contact with this surface water, dissolving or mixing physically with the water can be called surface water pollution.
3. Oxygen Depleting
Water bodies have micro-organisms. These include aerobic and anaerobic organisms. When to much biodegradable matter (things that easily decay) end up in water, it encourages more microorganism growth, and they use up more oxygen in the water. If oxygen is depleted, aerobic organisms die, and anaerobic organism grow more to produce harmful toxins such as ammonia and sulfides.
4. Ground water pollution
When humans apply pesticides and chemicals to soils, they are washed deep into the ground by rain water. This gets to underground water, causing pollution underground.
5. Microbiological
In many communities in the world, people drink untreated water (straight from a river or stream). Sometimes there is natural pollution caused by micro-organisms like viruses, bacteria and protozoa. This natural pollution can cause fishes and other water life to die. They can also cause serious illness to humans who drink from such waters.
6. Suspended Matter
Some pollutants (substances, particles and chemicals) do not easily dissolve in water. This kind of material is called particulate matter. Some suspended pollutants later settle under the water body. This can harm and even kill aquatic life that live at the floor of water bodies.
7. Chemical Water Pollution
Many industries and farmers work with chemicals that end up in water. This is common with Point-source Pollution. These include chemicals that are used to control weeds, insects and pests. Metals and solvents from industries can pollute water bodies. These are poisonous to many forms of aquatic life and may slow their development, make them infertile and kill them.
8. Oil Spillage
Oil spills usually have only a localized effect on wildlife but can spread for miles. The oil can cause the death to many fish and get stuck to the feathers of seabirds causing them to lose their ability to fly.
Water Pollution
The Ciliwung River is 119km long and passes through the Bogor Province, Depok District and the city of Jakarta in Indonesia. It is renowned for being one of the most heavily polluted rivers in the world. Many Indonesian citizens are forced to live by the river because it is all they can afford. Of the ten million people in Jakarta, half live on less than US$2 per day, and a large percentage of those people live along the Ciliwung. People that live along the Ciliwung use it for everything from washing themselves to cleaning clothes and dishes, to swimming. Contamination from human waste is the biggest cause of pollution in the Ciliwung. There is no organised rubbish collection for this area, so waste ends up in the river. Because they cannot afford clean drinking water, many of the residents are forced to boil and drink the water from the river, causing a raft of health problems. In 2009, a group of residents from Bogor with growing concerns about the river formed the Community Care for Ciliwung group ('Komunitas Peduli Ciliwung, or KPC). The group focuses its acitivities on picking up trash from the river every Saturday morning, and also facillitates other community activities such as tree planting days
Reflection: Global Citizen Workshop
Global Citizen definition - Citizens of the world have similar and different aspects, such as place of residence, language, religion, belief, culture, language, life and living. People who think about solutions helping mankind to through problems.
Personal Helps and Harms -
Help
Personal Helps and Harms -
Help
- Never buy water .
- Reduce the amount of meats eating per day .
- Buy recycled things .
Harms
- Leave the electronics turned on.
- Drink soda .
- Buy something that last long.
How can we connect class contents/discussions/skills/concepts with yesterday's workshop?
Global Citizen Workshop supports us to help the world ,by that we can relates it to sustainability .
Using less harmful stuffs and use recycled things or something that last longer.
What are some teaspoons of changes that you wish to implement?
I walk to school everyday instead of taking motorbike taxi in order to save money to do something else.
I want to bring my own bottle for water to school everyday to save money buying new water ,and we don't really have to worry about cleanness of our own bottle.
Monday, 24 November 2014
Biomes
Biome is Biological or any ecosystem. They are composed of physical factors such as temperature, humidity, and biological factors, such as plants and animals are similar spread in different geographical regions.
A biome is a collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions.
A biome is a collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions.
Biome can separate into 2 different kinds
1:Biome on land
2:Biome under the water
Biome on land divided into 7 categories.
1 Biome Tropical Rain Forest
2 Biome in the tropical deciduous forest
3 Biome Forest
4 Biome the temperate grasslands.
5 Biome Savannah
6 Biome of the sea
7 Biome Tundra
Biome in water divided into 3 types.
1 Biome freshwater
2 Biome sea
3 Biome brackish water
Tri Cellular Model of Atmospheric circulation
the tri cellular model helps explain the differences of in pressure belts, temperature, and precipitation that exists
Can be divided into three major cells
- Hadley -> Control weather over the tropics, where the air is warm and unstable
- Ferrel
- Polar
Tropical rainforest
- Rain forests have a very high diversity of animals and plants where they may have up to 480 species of trees
- It has constant high temperature and high rainfall throughout the year
- Estimated to produce 40 per cent of NPP of terrestrial ecosystems.
Tundra
- Most of the world’s tundra is found in the north polar region, aka arctic tundra.
- Rates of photosynthesis and productivity are low.
- The amount of water are also limited because the formation of ice
Dessert
- They cover 20-30 percent of land surface.
- Limits rates of photosynthesis and so rates of NPP are very low.
- Species in there are adapted, showing many xeophytic adaptations (adaptation to reduce water loss in dry conditions)
Temperature Forest
- Forest might contain only deciduous trees, only evergreens, or a mixture of both.
- Diversity is lower than in rainforest and the structure of temperate forest is simpler.
- Seasonal (has summer and winter) so there are two different tree types: evergreen (warm) and deciduous (cold)
Grassland
- Develop where there is not enough precipitation to support forests, but enough to prevent desert forming
- They are found in areas where the polar and Ferrel cells meet (mix the cold and warm air)
- Grasses grow beneath the surface and during cold periods, it can remain dormant until the ground warms.
Saturday, 22 November 2014
Savanna Far's Biome
What is it ?
-Another name is Savanna
-Made up of grasses and trees
-Is a grassland that have shrubs and trees that are isolated
-They are found between troipical rainforest and desert
Climate
-Tropical wet and dry climates
-Because tropical rainforest is wet and desert biome is dry
-Rain during summer and dry during winter
-In the dry season about four inches of rain will fall
Soil
-Porous,Sandy and dusty
-Has thin layer of humus
Location
-Located near the equator
-Between tropical rainforest and desert biome
-Africa, large areas of Australia ,South America and India
Animal Adaptations
-Small animal such as insects ,jack rabbit ,snakes prairie dogs etc
-Hide in the tall grass for protection against predator
-Large animal such as lion elephant and rhino
-Camoflage and speed facilitate
-Forming group
Zebra
-Live in herds
-Protected from natural predators -Because striped pattern makes it difficult to pick out a single target
Cheetah
-Have a spotted pattern to help hide them while they're stalking the sprey
-Can run up to 65mph
-Can stalk prey from long distance
-Another name is Savanna
-Made up of grasses and trees
-Is a grassland that have shrubs and trees that are isolated
-They are found between troipical rainforest and desert
Climate
-Tropical wet and dry climates
-Because tropical rainforest is wet and desert biome is dry
-Rain during summer and dry during winter
-In the dry season about four inches of rain will fall
Soil
-Porous,Sandy and dusty
-Has thin layer of humus
Location
-Located near the equator
-Between tropical rainforest and desert biome
-Africa, large areas of Australia ,South America and India
Animal Adaptations
-Small animal such as insects ,jack rabbit ,snakes prairie dogs etc
-Hide in the tall grass for protection against predator
-Large animal such as lion elephant and rhino
-Camoflage and speed facilitate
-Forming group
Zebra
-Live in herds
-Protected from natural predators -Because striped pattern makes it difficult to pick out a single target
Cheetah
-Have a spotted pattern to help hide them while they're stalking the sprey
-Can run up to 65mph
-Can stalk prey from long distance
Paper/Plastic Vivian's presentation
Plastic Bag
Plastic bag are made from non-renewable natural resources such as crude oil (petroleum) gas and coal.
Paper bags are made from trees
Advantages Paper bags
-They can hold more things than plastic bags
-They are renewable resources
-They are biodegradable
Disadvantages :Paper bags
-Production of papers bags requires a great amount of energy
-Paper production causes air pollution and deforestation
-The production of paper bags uses three times the amount of water it takes to make plastic bags
Advantages :Plastic Bags
-It requires 20-40% less energy to make 2 plastic bags
-They are cheap and light
Disadvantages :Plastic Bags
-Birds and other animals often mistake plastic bag as food
-Most plastic end up in landfill sometimes floating around in the air
-It takes hundred of years to decompose plastic bag
Paper takes lesser time to breakdown(biodegradable)
What is the issue ?
-Plasticc bags float around the oceans -one of the masses is about twice the size of texas located in North Pacific between America and Japan
-Over 100000 marine animals ,such as sea turtles ,whales and dolphins ,die every year because of plastic bags
-Plastic basg take from 400 to 1000 years to decompose
-Trees must be cut down to make paper bags ,which is one of the cause of deforestation
Solution
-Use cotton bags or jute bags
-Reuse plastic bags and paper bags
-Plastic bags acan be used as bin liners
-Start charging for plastic and
There is no perfect solution for this issue.
Monday, 17 November 2014
Estuaries Angel's Biome
What is Estuary ?
-A tidal mouth of a large river where the river meets the ocean
-Mixture of fresh water and slatwater
-Climate
-Changes through out season
-Soils
-High nutrients
-Location
-Hudson Bay estuary
Animals
-Fiddler Crabs
-American Shad
-Barnacles
-Osprey
-Blue Crab
Plants
-Sea grass
-Mangrove
-Cork grass
-Cattails
-Splatter Docks
Threats
-Pollution
-Dams
-But people are working to save there areas
-A tidal mouth of a large river where the river meets the ocean
-Mixture of fresh water and slatwater
-Climate
-Changes through out season
-Soils
-High nutrients
-Location
-Hudson Bay estuary
Animals
-Fiddler Crabs
-American Shad
-Barnacles
-Osprey
-Blue Crab
Plants
-Sea grass
-Mangrove
-Cork grass
-Cattails
-Splatter Docks
Threats
-Pollution
-Dams
-But people are working to save there areas
Water Resources
There are only 2.5% of fresh water all around the world that is directly accessible by humans populations.
The sustainability of freshwater resource usage
Humans require a lot water in daily life for drinking ,cooking or else without sustainable use ,human s will face many problems like some countries that are living without clean water to drink. And there are campaigns going on that support people to reuse the supplies such as bath water .
Quotes
1:No water ,no life .No blue ,no green -Sylvia Earle
2:I alone cannot change the world but I can cast a stone across the waters my ripples -Mother Teressa
Paper/Plastic Vivian Presentation
Plastic Bag
Plastic bag are made from non-renewable natural resources such as crude oil (petroleum) gas and coal.
Paper bags are made from trees
Advantages Paper bags
-They can hold more things than plastic bags
-They are renewable resources
-They are biodegradable
Disadvantages :Paper bags
-Production of papers bags requires a great amount of energy
-Paper production causes air pollution and deforestation
-The production of paper bags uses three times the amount of water it takes to make plastic bags
Advantages :Plastic Bags
-It requires 20-40% less energy to make 2 plastic bags
-They are cheap and light
Disadvantages :Plastic Bags
-Birds and other animals often mistake plastic bag as food
-Most plastic end up in landfill sometimes floating around in the air
-It takes hundred of years to decompose plastic bag
Paper takes lesser time to breakdown(biodegradable)
What is the issue ?
-Plasticc bags float around the oceans -one of the masses is about twice the size of texas located in North Pacific between America and Japan
-Over 100000 marine animals ,such as sea turtles ,whales and dolphins ,die every year because of plastic bags
-Plastic basg take from 400 to 1000 years to decompose
-Trees must be cut down to make paper bags ,which is one of the cause of deforestation
Solution
-Use cotton bags or jute bags
-Reuse plastic bags and paper bags
-Plastic bags acan be used as bin liners
-Start charging for plastic and per bags
Monday, 10 November 2014
Mugi's presentation .Deforestation ,Climate and Floods
Deforestation is the removal and cutting down of trees
6 causes
1:Agri-business
Its a business in order to raise cattle or grow cash crops like palm and soy which can be used in many producteds
2:Logging
-Building materials
-Comsumer products
3:Mining
It needs considereable amount of forest and land
4:Urbanizatiojn
Construction of road and housing because we have more people
5:Desertification
Because many industries in petrochemicals release their waste into the rivers which results in soil erosion and make it unfit to grow plants
6:Fire
-Extreme warm summers
-Milder winters
The ways to prevent deforestation
-Recycle
-Reforestation
-Farming Practice
-Limit the comsumption
-Use coal
-Support organization
Transpiration
It is a process by which the water is absorbed and released to the atmosphere
it occurs in order to carry the nutrients into plants from soil
Before the deforestation
1:Rain falls
2:Plant absorbs and transpires water
3:Water is released into the air
4:It forms clouds
5:It causes rain again
6:Rain falls
After the deforestation
Climate has changed
1:No tree can absorb and transpire the rainfall
2:Rain runs off the soil
3:Become a cause of floods and soil erosion
Actual Case 1
Yangtze River in China (1998)
-85% of forests in the Yangtze River basin were cut down
-Water flooded into areas where 400 million people lived in monsoon season
-More than 2000 people died
-At least 13 million people left their home
Actual Case 2
Ganges River in Bangladesh
-Deforestation in Himalaya mountain
-Few trees cannot prevent water and it directly flowed into the river
James Biome Polar
Climate soil and location
Climate -every months the polar area is about less than 10 degree Celsius
Soil :Ice and Snow
Location Antarctica
Animal in polar
Emperor penguin adaptations
-larger body to keep heat
-Short stiff tail to help balance on land
-Powerful claws on the feet
Behavioral adaptations
-They huddle together in the winter to conserve heat
-They bread during the winter so the baby will be independent in the summer
-The parents sit on the eggs to keep them warm
Weddell Seal
Adaptations
-The hind limbs have developed into flipper to swimming better
-Smooth shape to pass esaily through water
-Larger eyes to find foods
-Whiskers to help them feel in the dark
Behavioral Adaptations
-They have breath hole on the ice
-Can swim long distance
Polar Bear
Adaptations
-Long, stiff hair to keep them warm, and also help them swim in cold water
-Small and rounded ears so the cold water doesn't go in
-They become good at swimming
-They have thick layer of fat also to keep them warm
Artic Fox
Adaptation
-White fur to make the predator hard to see them
-Thick coat of fur to keep it warm
-Hair on the pads to help them walk on the snow
Walruses
Adaptations
-Good swimmer
-Body fat to keep them warm
-Bottoms of the flippers are bumpy to grip on ice
Polar plants
-Small
-Grow in a group or close together
-Grow low on the ground
-Some are black colour to absorb more light
-Some grow facing the sunlight
Threat
Climate changing :the ce are melting because its getting warmer
Pleng's presentation The Ocean
Facts: Marine Habitats
-More than 70% of the earth surface is covered by oceans
-The marine ecosystems can support many different living things in the ocean (such as habitats)
-It is also a major influence
Location
Ocean is divided in to 50 major oceans
-Atlantic Ocean
-Pacific Ocean
-Indian Ocean
-Southern Ocean
-Arctic Ocean
Ocean can also be divided into three vertical zones
-Euphotic zone =light can penetrate
-Disphotic zone = too deep for light to reach
-Aphotic zone = deepest part of the ocean (dark)
Weather
Marine biome influence the Earth by providing us
-rain = grow crops through evaporation
-Wind = help circulate the air
-Affects coastal/beachfront temperatures
Average temperature 4 C/ 39 F
Animal adaptation
-Jellyfish
=An umbrella shaped creatures
=Invertebrate
=They defend themselves by using their tentacles to protect
-Dolphin
=They migrate due to seasonal changes
=They prefer tropical climates but they do swim in cold water
=From a group called "pods"
-Blue Whale
=Fat tissue to make them warm
=Streamline shaped for swimming
=They eat krill (very small shrimp-like)
=Ventral grooves may expand
-Green Turtle
=Swim long distance
=They are herbivores (eat only plants)
{Depend on each species ,whether they are herbivores ,carnivores ,omnivores -based on their jaw structures
=Can be found in tropical and subtropical
-Grey Reef Shark
=Known as the Bronze Whaler Shark and Short Nose Blactail
=Found in warm and shallow waters near the coral reef
Plants Adaptations
-Algae is very important to the ocean
=it provides shelter and food for sea creatures
=We human also used in products like toothpaste and ice cream
-Marine plants algae provide supply and produce Oxygen
-Algae
=Known as seaweeds
=Many shapes and sizes
=Have cell wal structure and they can do photosynthetic like plants on land
-Green Algae (Chlorophyta)
=More than 4000 species
=Found
Wednesday, 5 November 2014
Thailand's Population challenges
-Thailand is now 61.5 million
68% of the population livwa is rural area
-Migration to bangkok had led to shortage of water land and an increase in pollution
-Stabilized population rate
-Fertility rate has gone down
Since the number of elders have increased due to less fertility rate
-The government provides social welfate assistance of 300 baht per month to older peeople having an annual income of less than 10000 baht
-Adults who take cate of their parents have been given entitlement to rax exemptions based on their income
Aging population
Population is stabilized
-People from the age of 65 and over is 10% at present and is expected to reach 22 in the next 10 years
The greatest callenge is providing long-term care for serverely disable people
Elderly Care
-Assistance can be claimed from the Thai Government if it is needed
-Accomodation and meals are provided at not cost to the resident but only for Thai citizens
-Total of 20 residential homes for the elderly and there are homes owned by private organizations in 7 provinces
-Bangkok
-Prathumthani
-Samutprakarn
-Sakolnakorn
-Saraburi
-Chonburi
-Arngthorng
Urbanization
-People are migrating from rural placing towards Bangkok to work during the dry season (mostly teenagers_
-Bigger paycheck
-Farmers that relied on traditional farming turned to machinge leabing the elderies with fewer jobs opportunites
-Some elders stay at villages because they don't want to the burden for their children
Solution
-Continue providing financial aids for elders
-Provide a system where couples get financial support if they have babies
-But these are problems that we are currently facing today
Compass Analysis
Should there be nuclear power plant
Nature
Yes, we can have it because it does not affect on the global worming or climate change (no air pollution)
No, if it is destroyed the nature environment would change and harm the lives (deforestation for building )
Economy
Yes, while construction it, people can get employed even after the construction .Cheap electricity bill. Low fuel cost -requires very little uranium
.continuous supply
No, need a lot of money to dispose off -needs long time of building .20 - 30 yers building it.
Society
Yes ,easy transportation .Reduces transport costs
No, unknown risks/accidents . Threat of destroying the power plant
Well-Being
Yes ,conserve energy for the future .Healthy for people
No, if accident happen, people might get sick because release of radioactivity
Should abortion be legal?
Nature
Yes, because less people use less resources
Should foreigners go to koh tao after the incident ?
Nature
Yes, because people will destroy the environment
Economy
No, because if people stop going to Koh Tao workers in there will lose their job .
Well-Being
Yes, because the situation like that can happen again
No, its a beautiful island and people can have fun with their friends
Should factory farming be legal ?
Nature
No, because wastes are turned in to pollution ,human are naturally forces animals to reproduce ,Ammonia is released from the waste that effects living organisms
Society
No,because it is unethical to torture animals and put them into harsh conditions
waste of resources to force feeding them with grains when we can use it for people who are in need
Harsh working condition
Well-Being
No, because they have been using anti-biotic to increase the rate of growth in animals
Less chance of having cancer and diseases
Factory farm animals carry on the diseases
Economy
Yes, because the largest providing income comes from factory farming in developing countries Philipines
Business wants to meet the needs
Not possible to produces as much meat when we consume
Time = money
people can get employed
Nature
Yes, we can have it because it does not affect on the global worming or climate change (no air pollution)
No, if it is destroyed the nature environment would change and harm the lives (deforestation for building )
Economy
Yes, while construction it, people can get employed even after the construction .Cheap electricity bill. Low fuel cost -requires very little uranium
.continuous supply
No, need a lot of money to dispose off -needs long time of building .20 - 30 yers building it.
Society
Yes ,easy transportation .Reduces transport costs
No, unknown risks/accidents . Threat of destroying the power plant
Well-Being
Yes ,conserve energy for the future .Healthy for people
No, if accident happen, people might get sick because release of radioactivity
Should abortion be legal?
Nature
Yes, because less people use less resources
Should foreigners go to koh tao after the incident ?
Nature
Yes, because people will destroy the environment
Economy
No, because if people stop going to Koh Tao workers in there will lose their job .
Well-Being
Yes, because the situation like that can happen again
No, its a beautiful island and people can have fun with their friends
Should factory farming be legal ?
Nature
No, because wastes are turned in to pollution ,human are naturally forces animals to reproduce ,Ammonia is released from the waste that effects living organisms
Society
No,because it is unethical to torture animals and put them into harsh conditions
waste of resources to force feeding them with grains when we can use it for people who are in need
Harsh working condition
Well-Being
No, because they have been using anti-biotic to increase the rate of growth in animals
Less chance of having cancer and diseases
Factory farm animals carry on the diseases
Economy
Yes, because the largest providing income comes from factory farming in developing countries Philipines
Business wants to meet the needs
Not possible to produces as much meat when we consume
Time = money
people can get employed
Sunday, 2 November 2014
Thailand's population challenges
-Thailand is now 61.5 million
68% of the population livwa is rural area
-Migration to bangkok had led to shortage of water land and an increase in pollution
-Stabilized population rate
-Fertility rate has gone down
Since the number of elders have increased due to less fertility rate
-The government provides social welfate assistance of 300 baht per month to older peeople having an annual income of less than 10000 baht
-Adults who take cate of their parents have been given entitlement to rax exemptions based on their income
Aging population
Population is stabilized
-People from the age of 65 and over is 10% at present and is expected to reach 22 in the next 10 years
The greatest callenge is providing long-term care for serverely disable people
Elderly Care
-Assistance can be claimed from the Thai Government if it is needed
-Accomodation and meals are provided at not cost to the resident but only for Thai citizens
-Total of 20 residential homes for the elderly and there are homes owned by private organizations in 7 provinces
-Bangkok
-Prathumthani
-Samutprakarn
-Sakolnakorn
-Saraburi
-Chonburi
-Arngthorng
Urbanization
-People are migrating from rural placing towards Bangkok to work during the dry season (mostly teenagers_
-Bigger paycheck
-Farmers that relied on traditional farming turned to machinge leabing the elderies with fewer jobs opportunites
-Some elders stay at villages because they don't want to the burden for their children
Solution
-Continue providing financial aids for elders
-Provide a system where couples get financial support if they have babies
-But these are problems that we are currently facing today
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)